by Lance Ralston | Apr 2, 2017 | English |
This episode is a bit different from our usual fare in that it’s devoted to the subject of art in Church History. It’s in no way intended to be a comprehensive review of religious art. We’ll take just a cursory look at the development of art in the early centuries.
Much has been written about the philosophy of art. And as anyone who’s taken an art history course in college knows, much debate has ensued over what defines art. It’s not our aim here to enter that fray, but instead of step back and simply chart the development of artistic expression in the First Centuries.
It’s to be expected the followers of Jesus would get around to using art as an expression of their faith quickly in Church History. Man is, after all, an emotional being and art is often the product of that emotion. People who would convert from headlong hedonism to an austere asceticism didn’t usually do so simply based on cold intellectualism. Strong emotions were involved. Those emotions often found their output in artistic expression.
Thus, we have Christian art. Emotions & the imagination are as much in need of redemption and capable of sanctification, as the reason and will. We’d better hope so, at least, or we’re all doomed to a grotesquely lopsided spiritual life. How sad it would be if the call to love God with all our heart, soul & mind didn’t extend to our creative faculty and art.
Indeed, the Christian believes the work of the Holy Spirit after her/his conversion, is to conform the believer into the very image of Christ. And since God is The Creator, it’s reasonable to assume the Spirit would bend humanity’s penchant for artifice to serve the glory of God and the enjoyment of man.
Scripture even says we are to worship God “in the beauty of holiness.” A review of the instructions for the making of the tabernacle make it clear God’s intention was that it be a thing of astounding beauty. And looked at from what we’d call a classical perspective, nearly all art aims to simply duplicate the beauty God as First Artist made when He spoke and the universe leapt into existence.
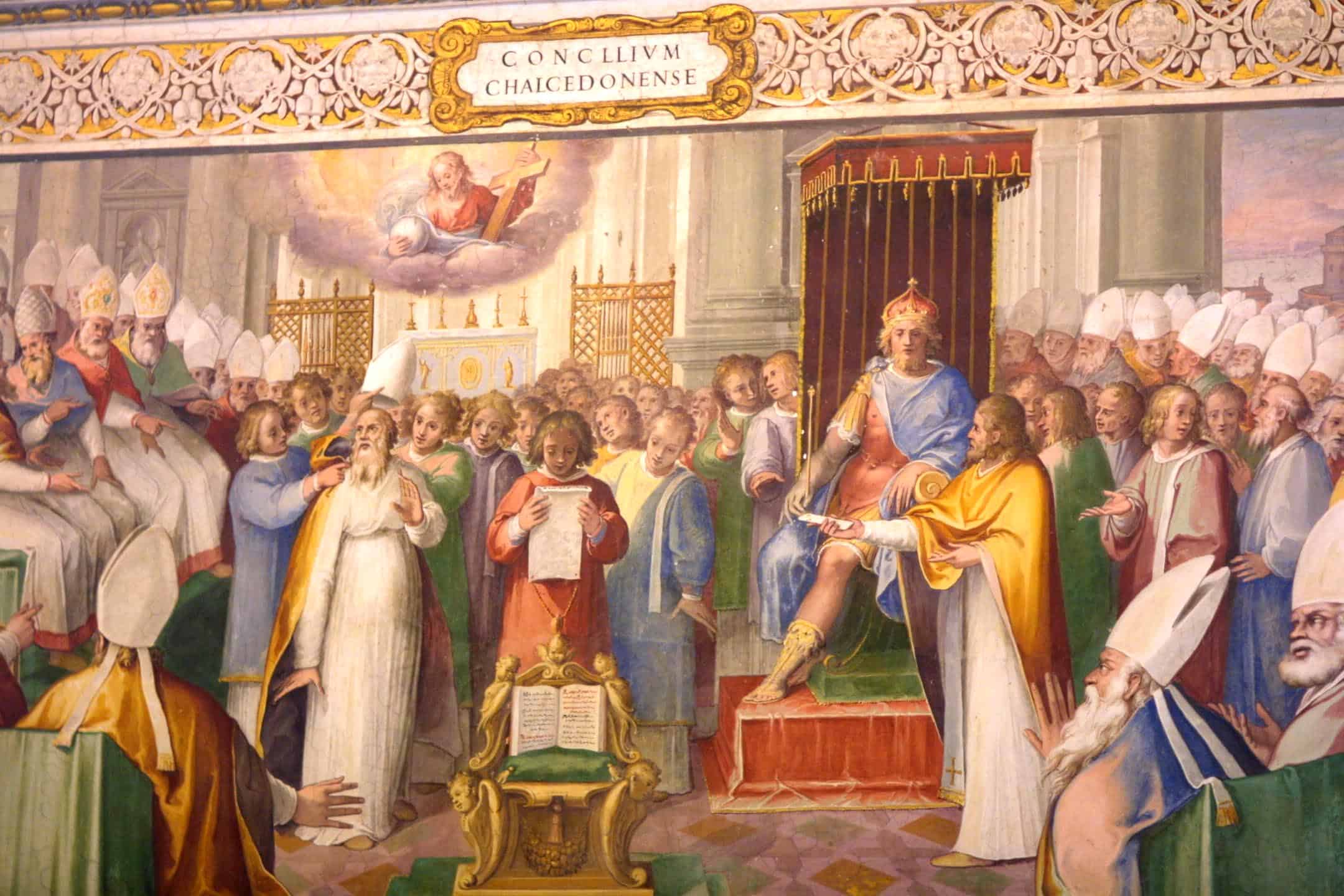
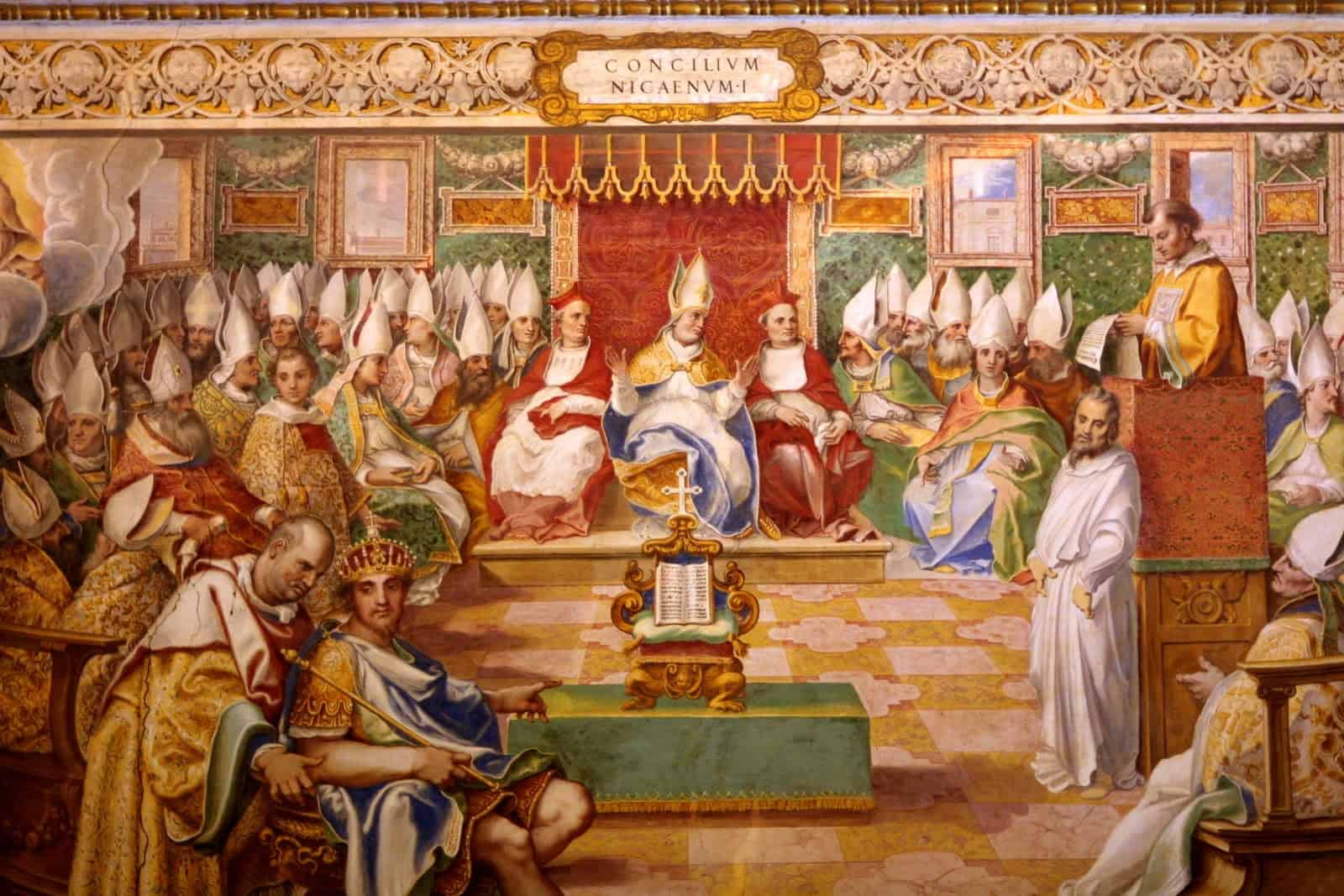
Historians tend to divide Early Church History into two large blocks using The First Council of Nicaea in 325 as the dividing line. The Ante-Nicaean Era runs from the time of the Apostles, the Apostolic Age, to Nicaea. Then the Post-Nicaean Era runs from the Council to The Medieval Era. This was the time of the first what are called 7 Ecumenical Councils; the last of which, is conveniently called the 2nd Nicaean Council, held in 787. So the Ante-Nicaean Era lasted only a couple hundred yrs while the Post-Nicaean Age was 500.
It would be nice if Art Historians would sync up their timelines to this plan, but they divide the history of Church Art differently. They refer to Pre-Constantinian Art, while From the 4th thru 7th Cs is called Early Christian Art.
The beginnings of identifiable Christian art are located in the last decades of the 2nd C. Now, it’s not difficult to imagine there’d been some artistic expression connected to believers before this; it’s just that we have no enduring record of it. Why is easy to surmise. Christians were a persecuted group and apart from some notable exceptions, were for the most part comprised of the lower classes. Christians simply didn’t want to draw attention to themselves on one hand, and on the other, there wasn’t a source of patronage base for art in service of the Gospel.
Another reason there wasn’t much art imagery generated before the 2nd C is because early generations of believers were mostly Jewish with a long-standing prohibition of making graven images, lest they violate the Commandments against idolatry. By the mid 2nd C, the Church had shifted to a primarily Gentile body. Gentiles had little cultural opposition to the use of images. Indeed, their prior paganism encouraged it. They quickly learned they were not to make idols, but had no reluctance to use images a symbols and representations to communicate the Gospel and express their faith.
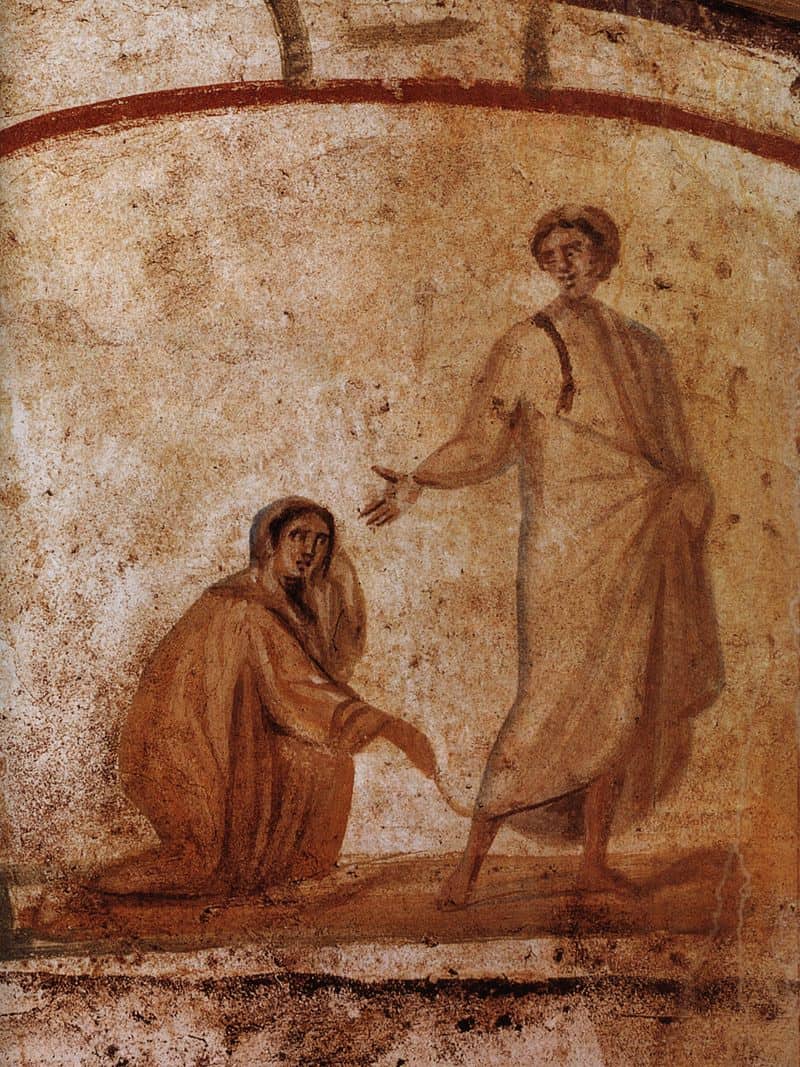
The style of this early art is drawn from Roman motifs of the Late Classical style and is found in association with the burial of believers. While pagans generally practiced cremation, the followers of Jesus shifted to burial as an expression of their hope in the Resurrection. So outside Rome’s walls near major roadways, numerous catacombs were excavated where Christians both met when the heat of persecution was up, and where their dead were interred. Some of the oldest of Christian imagery is a simple outline of a ship or an anchor scratched into the wall of a crypt. Both were symbols of the Church. The anchor is drawn from the NT Book of Hebrews which refers to the hope of the believer as an anchor or the soul. The ship was an apt picture for the Church. A vessel which is IN the Sea, but mustn’t have the sea in it, just as the Church is to be in the World, but the World is not to be in the Church. Another symbol used to make the resting place of Christians was the ubiquitous fish. As burial in the catacombs became de rigeur , families carved out entire rooms for the burial of their members. Bodies were placed in marble sarcophagi which over time were decorated with religious imagery; symbols and scenes drawn from Scripture.
Missing from the art crafted by Christians at this time are the scenes that will later become common. There’re few Nativity motifs, fewer crosses, and nothing depicting the resurrection. That’s not to say Christians in this early era didn’t regard the cross & resurrection as central to their faith. The writings of Ante-Nicene Fathers make it clear they did. It’s just that they hadn’t made their way into artistic expression yet. Rather than pointing DIRECTLY at Christ’s crucifixion & resurrection, artists instead used OT stories that foreshadowed the Gospel. Images of Abraham sacrificing Isaac, Jonah & the fish, Daniel in the lion’s den, Shadrach, Meshach, & Abed-Nego in the fiery furnace, as well as Moses striking the rock are all depicted in frescoes and tomb paintings.
The few images of Jesus from the Pre-Constantinian art we see him presented as The Good Shepherd, surrounded either by figures who likely represent the apostles, and symbols from nature, like peacocks, vines, doves and so on.
Nothing happened in the way of distinctly Christian architecture until Constantine for obvious reasons. Christians simply could not build their own places. When you’re trying to avoid attention due to persecution, engaging a construction project’s just not wise. But once The Faith was removed from the banned list, and the Rulers of Rome showed the emergent Faith favor, Christians began to shape their meeting places in a manner that maximized their utility, while also adorning them with imagery identifying them as dedicated to The Gospel. The discreet and out of the way places they’d met in before no longer served as suitable meeting places for the rapidly growing movement.
After Christianity was allowed to own property, it raised local churches across the Roman empire. There may have been more of this kind of building in the 4th C than there has been since, excepting during the 19th C in the United States. Constantine and his mother Helena led the way. The Emperor adorned not only his new city of Constantinople, but also embarked on a campaign to secure the assumed holy Places in the Middle East. Basilicas Churches were erected using funds from his personal account, as well as State funds. His successors, with the exception of Julian, called The Apostate, as well as bishops and wealthy laymen, vied with each other in building, beautifying, and enriching churches. The Faith that had not long before been a cause of great persecution, became a game to compete in; as the wealthy hoped to earn a higher place in heaven by the churches they raised. Churches became a venue for bragging rights. The Church Father Chrysostom lamented that the poor were being forgotten in favor of buildings, and recommended it wasn’t altars, but souls, God wanted. Jerome rebuked those who trampled over the needy to build a house of stone.
It might be assumed Christians would adopt the form for their buildings they were used to as pagans – a temple. Interestingly, they didn’t! Most pagan temples were relatively small affairs intended to hold little more than the idol of the god or goddess they were dedicated to. When pagans worshipped, they did so outdoors, often in a courtyard next to the temple. It wasn’t until the 7th C that believers began to re-purpose some of the larger now abandoned pagan temples for their own use. Even during Constantine’s time, Christians began to use layout of the secular basilica, the formal hall where a king or ruler would hold court.
The floor plan of one of these basilicas had a central rectangular hall, called a nave, with two side aisles. The main door was on one of the short sides of the nave, and on the opposite wall was the apse where a raised platform was built for the altar where the minister led the service.
During the 4th C saw Rome saw over 40 lrg churches built. In the New Rome of Constantinople, the Church of the Apostles and the Church of St. Sophia, originally built by Constantine, towered in majestic beauty. In the 5th C both were dramatically enlarged by Justinian.
As I said earlier, in the 7th C, the now abandoned pagan temples were turned over to Christians. Emperor Phocas gave the famous Pantheon to Roman’s bishop Boniface IV.
Anyone who’s been on a tour of Israel ought to be familiar with the term “Byzantine.” Because a good many of the ruins Christian tourists visit are labeled as Byzantine in architecture and era. The Byzantine style originated in the 6th C. and in the East continues to this day. It’s akin to the influence the French Classicism of Louis XIV had on Western architecture.
The main feature of the Byzantine style is a dome spanning the center of a floorplan that is cruciform. Let me see if I can help you picture this. Imagine a classic cross laid on the earth. The long bean is the central nave with the cross piece are the transverse sides used as side chapels. Suspended over the intersection of main & cross beams is a dome, decorated with frescoes of Biblically rich imagery.
Previous basilicas tended to be flat, blocky affairs; earthbound in their ponderance. The Byzantine basilica lifted the roof and drew the eye to that dome which seemed to pierce heaven itself. The eye was drawn upward. That idea will be perfected centuries later in the soaring ceilings and arches of Europe’s Gothic cathedrals.
The most perfect execution of the Byzantine style is found in the Hagia Sophia, the Church of Holy Wisdom in Istanbul. It was built by the Emperor Justinian in the 6th C on the plans of Anthemius & Isidore. It’s 220’ wide, 252’ long; with a 180’ diameter dome supported by four gigantic columns, rising 169’ over the central altar. The dome is so constructed that the court biographer Procopius describes it as being suspended form heaven by golden chains.
The cross, which today stands as the universal symbol for Christianity, wasn’t used in artifice until at least the late 4th C. The historical record suggest Christians made the sign of the cross on their foreheads, over their eyes, mouths, & hearts as early as the 2nd C. But they didn’t make permanent images of it till later. And then we find some church father urging Christians not to make magical talisman of them.
Julian accused Christians of worshipping the cross. Chrysostom wrote, “The sign of universal detestation, the sign of extreme penalty, has become an object of desire and love. We see it everywhere; on houses, roofs, walls, in cities and villages, in markets, along roads, in deserts, on mountains & in valleys, on the sea, ships, books, weapons, garments, in honeymoon chambers, at banquets, on gold & silver vessels, engraved on pearls, in paintings, on beds, the bodies of sick animals, & the possessed, at dances of the merry, and in the brotherhoods of monks.”
It isn’t till the 5th C that we find the use of the crucifix; that is a cross that isn’t bare. It now holds the figure of the impaled Christ.